Morphology and morphometry of adult phase of Centrocestus formosanus (Digenea: Heterophyidae) from metacercariae of channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29059/cvpa.v1i2.14Keywords:
digenean, fish, metacercaria, helminthsAbstract
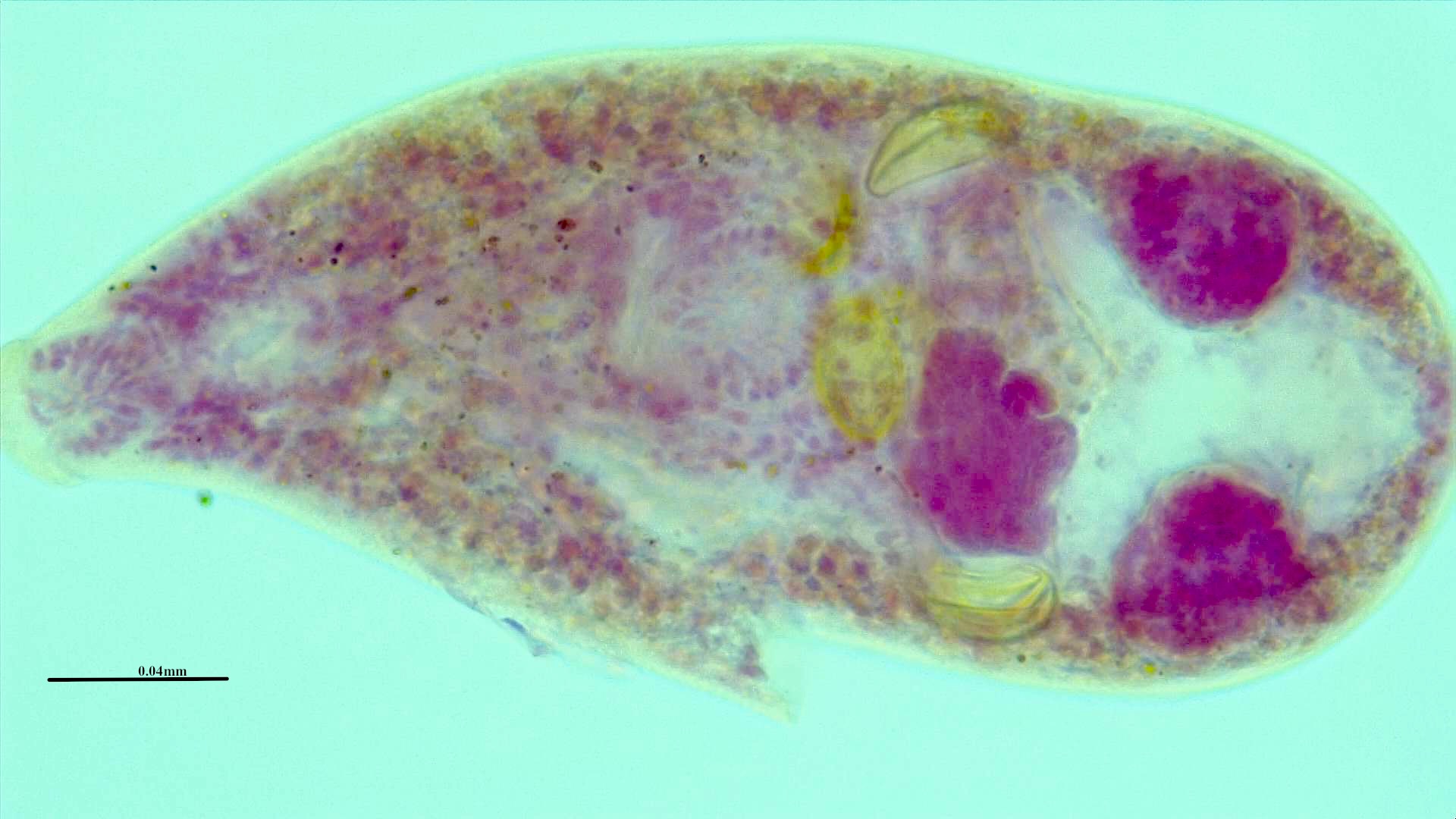
With the aim of obtaining the adult phase of Centrocestus formosanus, two mice were feed with juvenile Ictalurus punctatus (from a hatchery in Tamaulipas, Mexico) gills, which were infected with C. formosanus metacercariae. After seven days, mice were euthanized and parasites found in the digestive tract were fixed, and conserved in 70% alcohol. Parasites were processed with standard protocols for flatworms. The specimens obtained fit morphological and morphometrically with Centrocestus formosanus. In the present manuscript morphometric data not previously considered are reported. To our knowledge, this is the first study of adults of C. formosanus obtained experimentally of metacercariae from channel catfish.
References
Aguilar-Aguilar, R., Martínez-Aquino, A., Pérez-Rodríguez, R., Pérez-Ponce-de-León, G. (2009). Digenea, Heterophydae, Centrocestus formosanus (Nishigori, 1924) metacercariae:Distribution extension for Mexico, new state record, and geographic distribution map. CheckList 5 (2), 357-359. https://doi.org/10.15560/5.2.357
Arguedas, C. D., Dolz, G., Romero-Zúñiga, J. J., Jiménez-Rocha, A. E., & León-Alán, D. (2010). Centrocestus formosanus (Opisthorchiida: Heterophyidae) as a cause of death in graytilapia fry Oreochromis niloticus (Perciforme: Cichlidae) in the dry Pacific of Costa Rica. Revista de Biología Tropical, 58, 1453-1465.
Arizmendi-Espinosa, M. A. (1992). Descripción de algunas etapas larvarias y de la fase adulta de Centrocestus formosanus de Tezontepec de Aldama, Hidalgo. Anales Instituto de Biología.UNAM, Serie Zoología, 63 (1), 1-11.
Boerlage, A. S., Graat, E. A. M., Verreth, J. A., & De Jong, M. C. M. (2014). Transmission offish-borne zoonotic trematodes (Heterophyidae) to common carp (Cyprinus carpio) is independent of density of fish and trematodes. Journal of Helminthology, 88, 183–188. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X12000910
Bray, R. A., Gibson, D. I., & Jones, A. (Eds.) (2008): Keys to the Trematoda Vol. 3. CABInternational and Natural History Museum.
Cantu, V., Brandt, T. M., & Arsuffi, T. L. (2013). An evaluation of three sampling methods tomonitor a digenetic trematode Centrocestus formosanus in a spring-fed ecosystem.Parasitology, 140, 814-820. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182013000085
Chai, J. Y., De, N. V., & Sohn, W. M. (2012). Foodborne trematode metacercariae in fish fromNorthern Vietnam and their adults recovered from experimental hamsters. Korean Journalof Parasitology, 50, 317-325. https//doi:10.3347/kjp.2012.50.4.317
Chai, J. Y., Sohn, W. M., Yong, T. S., Eom, K. S., Min, D. Y., Lee, M. Y., Lim, H., Insisiengmay,B., Phommasack, B., & Rim, H. J. (2013). Centrocestus formosanus (Heterophyidae):human infections and the infection source in Lao PDR. Journal of Parasitology, 99,531-536. https://doi.org/10.1645/12-37.1
Gjurcevic, E., Petrinec, Z., Kozaric, Z., Kuzir, S., Kantura, V. G., Vucemilo, M., & Dzaja, P. (2007).Metacercariae of Centrocestus formosanus in goldfish (Carassius auratus L.) imported into Croatia. Helminthologia, 44, 214-216. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11687-007-0034-4
Han, E. T., Shin E. H., Phommakorn S., Sengvilaykham B., Kim J. L., Rim, H. J., & Chai, J. Y.(2008). Centrocestus formosanus (Digenea: Heterophyidae) encysted in the fresh waterfish, Puntius brevis, from Lao PDR. Korean Journal of Parasitology, 46 (1), 49–53. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2008.46.1.49
Hernández, L. E., Díaz, M. T., & Bashirullah, A. D. (2003). Description of different development alstages of Centrocestus formosanus (Nishigori, 1924) (Digenea: Heterophyidae). Revista Científica, FCV-LUZ, XIII (4):285-292.
Hop, N. T., De, N.V., Murrell, D., & Dalsgaard, A. (2007). Occurrence and species distribution offish borne zoonotic trematodes in wastewater-fed aquaculture in northern Vietnam. TropicalMedicine & International Health, 12, 66-72. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3156.2007.01943.x
Knoff, M., Pinto, R. M., Clemente S. C. D., Fonseca, M. C. G., & Gomes, D. C. (2011). Diphyllobothrium latum and Diphyllobothrium sp. as the agents of Diphyllobothriasis in Brazil: morphological analysis and of two new case reports. Revista Brasileira de Medicina Veterinária, 33, 159-164.
Li, M. H., Huang, H. I., Chen, P. L., Huang, C. H., Chen, Y. H., & Ooi, H. K. (2013). Metagonimus yokogawai: metacercariae survey in fishes and its development to adult worms in various rodents. Parasitology Research, 112, 1647-1653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3320-8
Mati, V. L. T, Pinto, H. A., & de Melo, A. L. (2013). Experimental infections of Swiss and AKR/Jmice with Centrocestus formosanus (Trematoda: Heterophyidae). Revista do Instituto de Medicina Tropical de São Paulo, 55, 133-136. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0036-46652013000200013
Mitchell, A. J., Goodwin, A. E., Salmon, M. J., & Brandt, T. M. (2002). Experimental infectionof an exotic heterophyid trematode, Centrocestus formosanus, in four aquaculture fishes.North American Journal of Aquaculture, 64, 55-59. https://doi10.1577/1548-8454(2002)064
Mitchell, A. J., Overstreet, R. M., Goodwin, A. E., & Brandt, T. M. (2005). Spread of an exotic fish-gill trematode: A far-reaching and complex problem. Fisheries, 30, 11-16.
Mitchell, A. J., Salmon, M. J., Huffman, D. G., Goodwin, A. E., & Brandt, T. M. (2000). Prevalenceand pathogenicity of a heterophyid trematode infecting the gills of an endangered fish, thefountain darter, in two central Texas spring-fed rivers. Journal of Aquatic Animal Health, 12,283-289. http://dx.doi.org/10.1577/1548-8667(2000)012%3C0283:PAPOAH%
Nguyen, V. D., & Thanh, H. L. (2011). Human infections of fish-borne trematodes in Vietnam: Prevalence and molecular specific identification at an endemic commune in Nam Dinh province. Experimental Parasitology, 129, 355-361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2011.09.005
Paperna, I., & Dzikowski, R. (2006). Digenea (Phylum Platyhelminthes). En: P.T.K. Woo (Ed.)Fish Diseases and Disorders, Protozoan and Metazoan Infections Vol. 1. (pp. 355-390.).CAB International.
Pérez-Ponce de León, G., García-Prieto, L., & Mendoza-Garfias, B. (2007). Trematode parasites (Platyhelminthes) of wildlife vertebrates in Mexico. Zootaxa, 1534, 1-247. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.1534.1.1
Pinto, H. A., & de Melo, A. L. (2010) Melanoides tuberculata (Mollusca:Thiaridae) as an intermediat host of Centrocestus formosanus (Trematoda: Heterophyidae) in Brazil. Revista do Instituto de Medicina Tropical de São Paulo, 52, 207-210. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0036-46652010000400008
Pinto, H .A., Mati, V. L. T., & de Melo, A. L. (2015). Experimental centrocestiasis: Worm burden, morphology and fecundity of Centrocestus formosanus (Trematoda: Heterophyidae) indexamethasone immunosuppressed mice. Parasitology International, 64, 236-239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2015.02.002
Pinto, H. A., Gonçalves, N. Q., López-Hernandez, D., Pulido-Murillo, E. A., & de Melo, A. L.(2018). The life cycle of a zoonotic parasite reassessed: Experimental infection of Melanoidestuberculata (Mollusca: Thiaridae) with Centrocestus formosanus (Trematoda: Heterophyidae).PloS one, 13(4), e0194161. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0194161
Pritchard, M. H., & Kruse, G. O. W. (1982). The Collection and Preservation of Animal Parasites. University of Nebraska Press.
Rábago-Castro, J. L., Sánchez-Martínez, J. G., Loredo-Osti, J., Gómez-Flores, R., Tamez-Guerra,P., & Ramírez-Pfeiffer, C. (2011). Temporal and spatial variations of ectoparasites oncage-reared channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus, in Tamaulipas, Mexico. Journal of the World Aquaculture Society, 42, 406-411. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-7345.2011.00480.x
Rosas-Valdez, R., & Pérez-Ponce de León, G. 2008. (2008). Composición taxonómica de los helmintos parásitos de ictalúridos y heptaptéridos (Osteichthyes: Siluriformes) de México, con una hipótesis de homología biogeográfica primaria. Revista Mexicana de Biodiversidad, 79, 473-499.
Schell S. C. (1970). The Trematodes. W. M. C. Brown Company Publishers.
Scholz, T., & Salgado-Maldonado, G. (2000). The introduction and dispersal of Centrocestus formosanus (Nishigori, 1924) (Digenea: Heterophyidae) in Mexico: A review. AmericanMidland Naturalist, 143, 185-200. http://dx.doi.org/10.1674/0003-0031(2000)143%5b0185:TIADOC%
Velásquez, L. E., Bedoya, J. C., Areiza, A., & Vélez, I. (2006). Primer registro de Centrocestus formosanus (Digenea: Heterophyidae) en Colombia. Revista Mexicana de Biodiversidad, 77, 119-121.
Yousif, F., Ayoub, M., Tadros, M., & El Bardicy, S. (2016). The first record of Centrocestus formosanus (Nishigori, 1924) (Digenea: Heterophyidae) in Egypt. Experimental Parasitology, 168, 56-654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2016.06.007
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Ciencias Veterinarias y Producción Animal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Accepted 2024-01-22
Published 2024-01-31







